-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 32
3D Sod 256
This is a higher resolution version of the sod shock test, with a grid of 256x256x256.Parameters from Sod (1978).
Illustrates the ability of a code to resolve shocks and contact discontinuities over a narrow region. The test consists of two constant states (on left pressure and density are equal to 1; on right they are equal to 0.1) separated by a discontinuity at 0.5. Gamma is set to 1.4. This test is performed with the default hydro build (cholla/builds/make.type.hydro) and Van Leer integrator.
#
# Parameter File for 3D Sod Shock tube
#
################################################
# number of grid cells in the x dimension
nx=256
# number of grid cells in the y dimension
ny=256
# number of grid cells in the z dimension
nz=256
# final output time
tout=0.2
# time interval for output
outstep=0.2
# name of initial conditions
init=Riemann
#init=Read_Grid
# domain properties
xmin=0.0
ymin=0.0
zmin=0.0
xlen=1.0
ylen=1.0
zlen=1.0
# type of boundary conditions
xl_bcnd=3
xu_bcnd=3
yl_bcnd=3
yu_bcnd=3
zl_bcnd=3
zu_bcnd=3
# path to output directory
outdir=./
#################################################
# Parameters for 1D Riemann problems
# density of left state
rho_l=1.0
# velocity of left state
vx_l=0.0
vy_l=0.0
vz_l=0.0
# pressure of left state
P_l=1.0
# density of right state
rho_r=0.1
# velocity of right state
vx_r=0.0
vy_r=0.0
vz_r=0.0
# pressure of right state
P_r=0.1
# location of initial discontinuity
diaph=0.5
# value of gamma
gamma=1.4
Upon completion, you should obtain two output files. The initial and final densities (in code units) of a slice along the y-midplane is shown below. Examples of how to plot projections and slices can be found in cholla/python_scripts/Projection_Slice_Tutorial.ipynb.
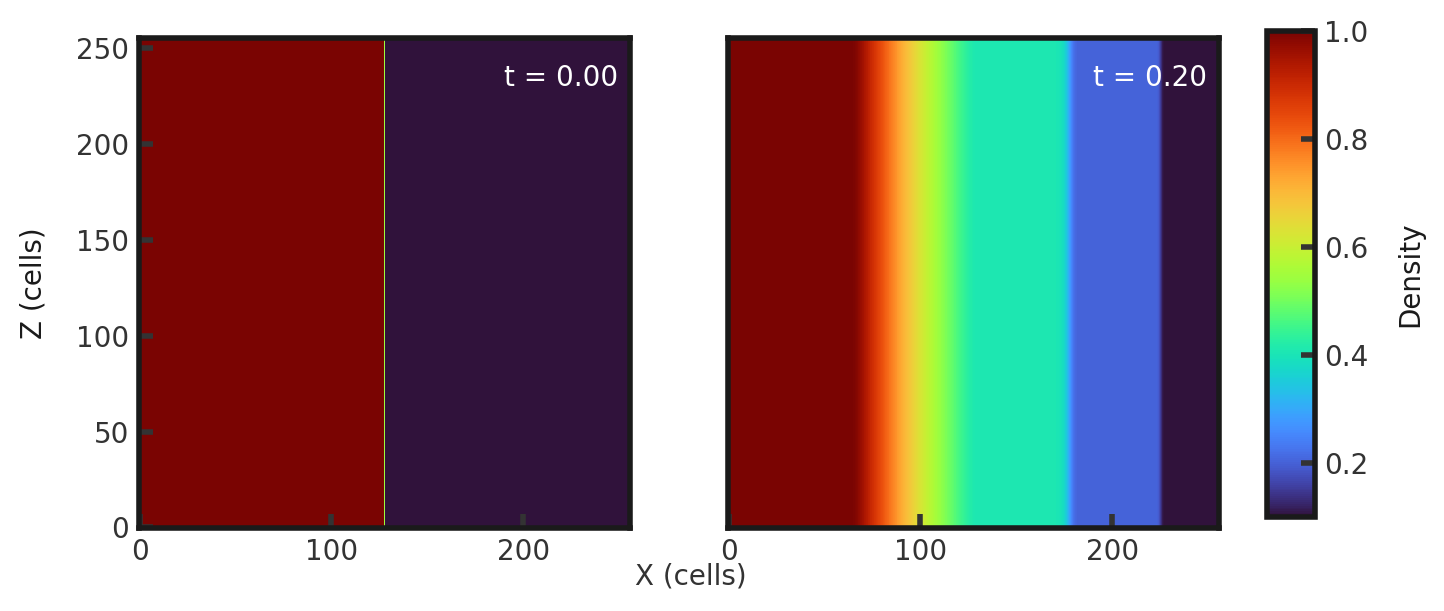
We see a smoother density gradient within the rarefaction wave due to the higher resolution.
A skewer in x along the y and z midplanes yields the traditional 1-dimension solution shown below (pink dots) plotted over the exact solution (purple line).:
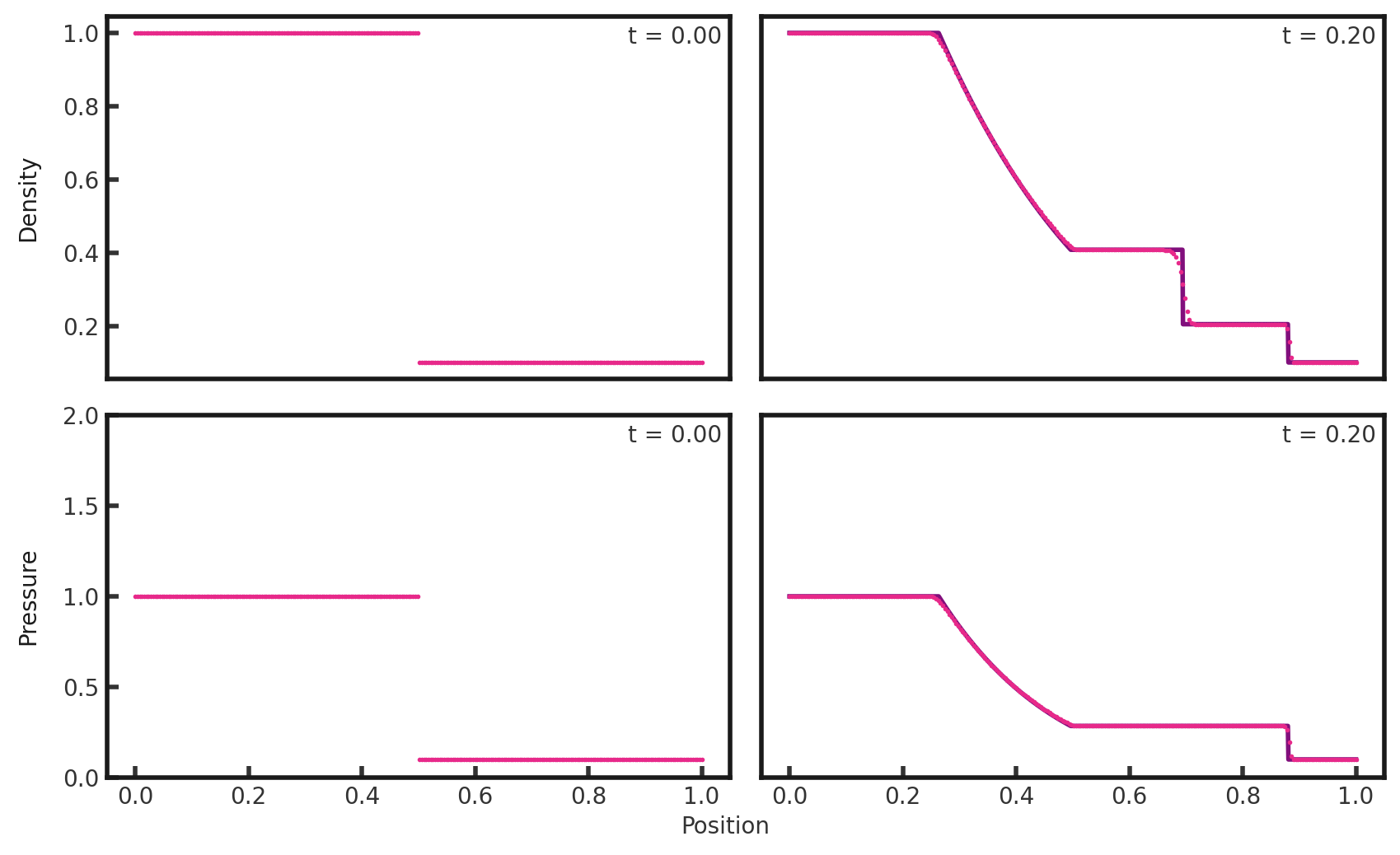
We can see a rarefaction wave on the left side, followed first by a contact discontinuity and then a shock. Transitions between shocks are resolved more narrowly.