This lab hands-on manual guides you to build a simple password generator using basic Python programming only.
This guide will not cover the basics of Python programming like what Python is, the IDEs to use and the general syntax. It will just show the steps to build the generator in Python.
You can use online IDE like Replit to start this project. Once you are ready with your IDE, you may start from Step 01.
Test if the Python compiler is running properly by printing out a "Hello World" in the console using the following code:
print('Hello World')When the "Hello World" is printed out in the console successfully, we can remove both testing lines and start building our generator in the next step.
We can get user input to determine the desired length of password generated using the code below:
# Set Password Length, Convert to Integer
password_length = int(input('Enter password length: '))We place the input() method inside int() to parse the value entered by the user into integer datatype.
A strong password usually contains each of the following types of character:
- Uppercase Letter
- Lowercase Letter
- Digits
- Special Characters
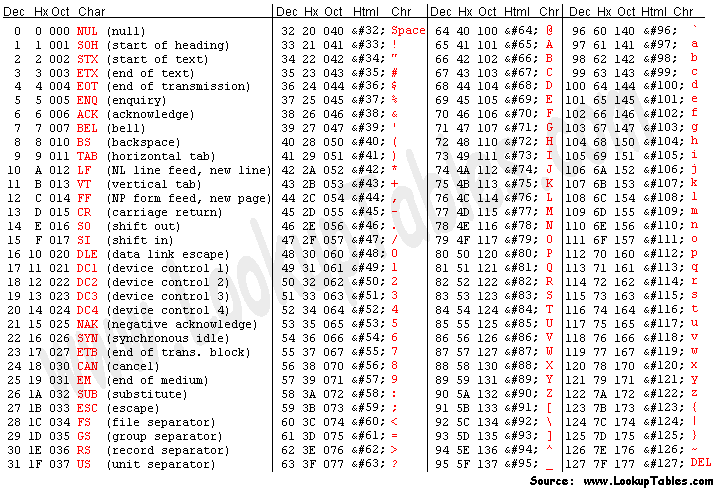
We can access each of them (except Special Characters) by using the ASCII table.
We can obtain the characters using their respective decimal equivalent (DEC) in the ASCII table with chr(DEC).
To obtain a random character within each's range, we will need to import the random library first using the code below:
import randomWe will need to import it at the start of the code so that it can be accessed then. Now that we have the random library within our code, we can get a random character of each type's with the code below:
# Upper Case Character
random_upper_case_character = chr(random.randint(65, 90))
# Lower Case Character
random_lower_case_character = chr(random.randint(97, 122))
# Digit Character
random_digit_character = chr(random.randint(48, 57))However, special characters are distributed across the ASCII Table and there is no one specific range that includes all of them, hence we will be tackling this with another way.
Below is the list of special characters according to this link.
# Set Constants
SPECIAL_CHARACTERS = '!"#$%&\'()*+,-./:;<=>?@[\]^_`{|}~'Then, we can get a random character within this string using the code below, and add it after the random character generator above:
# Special Character
random_special_character = SPECIAL_CHARACTERS[random.randint(0, len(SPECIAL_CHARACTERS) - 1)]Our approach here is to get almost even amount of each inside our password by using the round-robin approach, where we will add one character of each type then add another character of each type until we reach the length desired by the user.
We will first create an empty character array to store all characters during the round-robin:
password_character_arr = []Then, we will use a for loop for the round-robin as shown in the code below, which we have included the random generation of each character within the if-elif-else conditions:
for i in range(length):
# Upper Case Character
if (i % 4 == 0):
random_upper_case_character = chr(random.randint(65, 90))
password_character_arr.append(random_upper_case_character)
# Lower Case Character
elif (i % 4 == 1):
random_lower_case_character = chr(random.randint(97, 122))
password_character_arr.append(random_lower_case_character)
# Digit Character
elif (i % 4 == 2):
random_digit_character = chr(random.randint(48, 57))
password_character_arr.append(random_digit_character)
# Special Character
else:
random_special_character = SPECIAL_CHARACTERS[random.randint(0, len(SPECIAL_CHARACTERS) - 1)]
password_character_arr.append(random_special_character)Now that we have all of the characters in our password_character_arr, we can shuffle its content by using the code below:
# Reshuffle Password Characters
random.shuffle(password_character_arr)Then, we will also need to join the characters in the array into a string, which can be done using the join() method.
# Join Array Elements into String
password_final = ''.join(password_character_arr)The '' in front of the join() method means that the characters are joined together separated by '' which technically means no separation.
Lastly, we can just display the generated strong password in the output using the code below:
# Display Password
print(f'Generated Password: {password_final}')On paper we are done with the project, but there is a bug.
In the input() method previously where we allow users to enter the desired length of their password, there is a possibility that the user entered values outside of our expectation, hence we can perform validation using a while loop.
The concept behind this is to reask the user to enter a valid input until a valid input is reached.
# Length Validation
while length < 4 or length > 64:
print('The length of password must be at least 4! Try again.')
length = int(input('Enter Password Length: '))In this case, we limit the accepted value for length to be between the range of 4 and 64 inclusive, since 4 means that our password has each of the character type to be a strong password, and 64 is usually the maximum length of a password.
Now that you have finished creating the password generator, you may used it to update your weaker passwords occasionally.
This project guide is created and owned by LimJY03, licensed under Apache License 2.0.