- Core Java - Overview, First Java Program, Variables, Datatypes, Literals, Operators, Expressions and Conditional Statements. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/java-programming-basics/
- Core Java - String, Arrays, Looping Statements, Methods, Class, Object, static https://www.programiz.com/java-programming
- Core Java - Access Modifiers, Packages, Encapsulation https://www.javatpoint.com/inheritance-in-java
- Core Java - Polymorphism, Inheritance, Abstraction, Interface https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/polymorphism-in-java/
- Core Java - Collection Framework, ArrayList, Map, Set. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/collections-in-java-2/
- Core Java - File Handling, Threads and Garbage Collections, Exception Handling, Enums. https://www.javatpoint.com/java-io
- Java 8 - Java 8 Features - Lambda Expressions, Streams, Filters, java.time. https://www.journaldev.com/2389/java-8-features-with-examples
- Junit 5 and Maven - Writing basic tests, Assert Statements, Testing Exceptions https://howtodoinjava.com/junit-5-tutorial/
- RDBMS - DDL Commands, DML Commands https://www.javatpoint.com/mysql-tutorial
- RDBMS - Operators, Aggregate, String, Date Functions https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/sql-tutorial/
- Web Basics - Learn the basics of HTML5 & CSS3 https://www.w3schools.com/html/
- JavaScript - Learn the basics of Javascript https://www.javatpoint.com/javascript-tutorial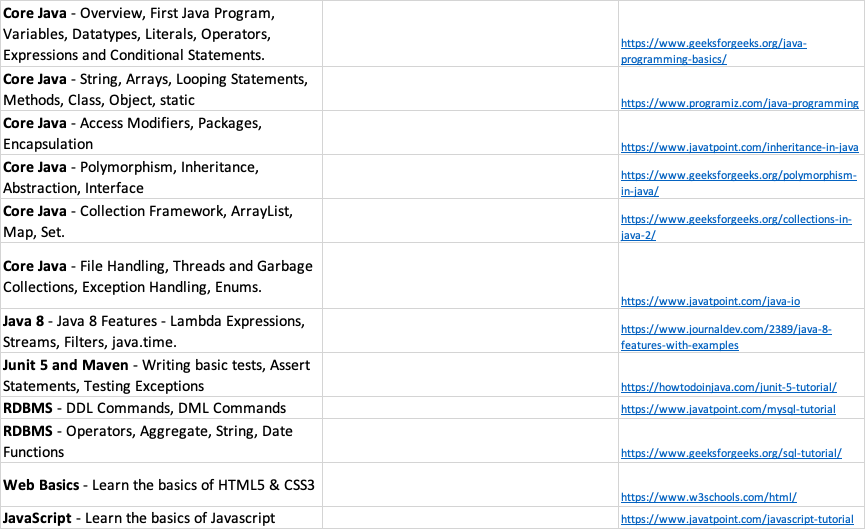
Java -
Required softwares and tools -
----------------------------------
JDK - 11+
MySQL - 8
IDEs - Eclipse(Spring Tools IDE), Visual Studio Code
----------------------------------------------------
Java -
* Object Oriented
* Dynamic
* Platform Independent
JDK - Java Developmemt Kit
JRE - Java Runtime Environment
JVM - Java Virtual Machine
----------------------------------------
Basic building blocks in Java
-----------------------------------------
keywords,
identifiers
literals,
variables,
methods,
classes,
objects
---------------------------------------
Using variables in java:
-----------------------------
data-type variable-name;
Data-types
-------------------
Primary :
----------
byte - 1 byte integer value
short - 2 bytes integer value
int - 4 bytes
long - 8 bytes
float - 4 bytes (20.67F, -0.00054f)
double - 8 bytes (20.54630817)
char - 1 Byte / 2 Bytes ('a','-','5')
boolean - 1 Bit (true/false)
Secondary :
--------------
arrays
enum
User defined types:
-------------------
class
interface
Java Naming Standard :
------------------------
Class naming rule :
----------------------
Should always start with an Uppercase and follow the Camel casing
- Scanner, BufferedReader
Variables/Method naming rule :
-------------------------------
Should always start with a lowercase and follow the Camel casing
- main(),username, nextInt()
Package naming rules :
-----------------------
Should be in lowercase only
Final fields/constants :
--------------------------
Should be in uppercase only
final double PI=3.14;
-- Complete the first four challenges -- https://www.hackerrank.com/domains/java
- Core Java - Overview, First Java Program, Variables, Datatypes, Literals, Operators, Expressions and Conditional Statements. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/java-programming-basics/
- Core Java - String, Arrays, Looping Statements, Methods, Class, Object, static https://www.programiz.com/java-programming
- Core Java - Access Modifiers, Packages, Encapsulation https://www.javatpoint.com/inheritance-in-java
- Core Java - Polymorphism, Inheritance, Abstraction, Interface https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/polymorphism-in-java/
- Core Java - Collection Framework, ArrayList, Map, Set. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/collections-in-java-2/
- Core Java - File Handling, Threads and Garbage Collections, Exception Handling, Enums. https://www.javatpoint.com/java-io
- Java 8 - Java 8 Features - Lambda Expressions, Streams, Filters, java.time. https://www.journaldev.com/2389/java-8-features-with-examples
- Junit 5 and Maven - Writing basic tests, Assert Statements, Testing Exceptions https://howtodoinjava.com/junit-5-tutorial/
- RDBMS - DDL Commands, DML Commands https://www.javatpoint.com/mysql-tutorial
- RDBMS - Operators, Aggregate, String, Date Functions https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/sql-tutorial/
- Web Basics - Learn the basics of HTML5 & CSS3 https://www.w3schools.com/html/
- JavaScript - Learn the basics of Javascript https://www.javatpoint.com/javascript-tutorial
Inheritance
--------------
Item - name, price, id
Phone - ram, storage
Laptop - ram, storage, os
Vehicle - super class [name,regno]
/ \ \
/ \ \
/ \ \
Bus Car Bike - sub class
[capacity] /\
/ \
Electric Petrol
bus - horn()
car - musicSystem, play()
bike - boolean abs, accletate()
Car car = new Vehicle();
class Item{
....
....
}
class Laptop extends Item{
}
** private and static properties wont be inherited
Abstraction:
--------------
Item -
id, name, price
abstract void showItemDetails();
setPrice()
ElectronicItem extends Item -
showItemDetails()
...
Clothing extends Item -
showItemDetails()
...
Abstract Class -
contains abstract methods
cannot create object of any abstract class
extending the abstract class and overriding the abstrat methods are necessary
Multiple Inheritance :
------------------------
A B
\ /
\ /
C
A{
fun(){
...
}
}
B{
fun(){
...
}
}
class C extends A,B{
}
Interfaces -
------------------
an interface looks like a class but it can have only abstract methods and final fields
When to choose abstract class over interface and vice versa?
-------------------------------------------------------------
Item - price, name
WrittenItem extends Item - author
Book extends WrittenItem - isbn, pages
Journal extends WrittenItem - publishedDate
MediaItem extends Item
....
Interfaces are used for runtime ploymorphism and to acheive loose coupling
Method Overloading
----------------------
method with same name but different signatures within the same class
- no of arguments, type of arguments
class Calculator{
int add(int a, int b){
return a+b;
}
int add(int a, int b, int c){
return a+b+c;
}
float add(float a, float b){
return a+b;
}
}
main(){
Calculator calc = new Calculator();
calc.add(4,5);
calc.add(4.5f,3.4F);
calc.add(3,8,6);
}
notes.txt
lotus.jpg
profile.pdf
Overloading vs Overriding
---------------------------
Object class methods :
-------------------------
String toString()
boolean equals()
int hashCode()
Collection Framework
-------------------------
Limitations of Arrays -
* Fixed size
* Items can not be removed
* Accessing through index only
* no well define algorithms are present
Collection Framework
--------------------
API - Application Programming Interface
Consists of different interfaces and classes
Layered Architecture
----------------------
Presentation Layer - For interactiong with clients
Business Layer - Business Logic and service classes
Persistence Layer - DAO (Data Access Object) contains storage logic
Database - Conatins the database
DBMS - Database Management System
Relational
------------
MySQL, SQLServer, Oracle, Postgres
Non-Relational (NoSQL)
-----------------------
MongoDB, Amazon DynamoDB
SQL - Structured Query Language
-------------------------------
Employee, Student, Laptop - Entities
Tables - Rows/Records/Tuple | Columns/Fields/Attributes
-----------------
SQL
------
DDL - Data Defn. Language
- create, alter, drop, truncate
DML - Data Manipulation Language
- insert, update, delete
DQL - Data Query Language
- select
DCL - Data Control Language
- grant, revoke
TCL - Transaction Control Language
- COMMIT, ROLLBACK, SAVEPOINT
empno - numeric(4)
ename - varchar(30)
job - varchar(30)
hiredate - date
mgr - numeric(4)
sal - numeric(6,2)
comm - numeric (6,2)
deptno - numeric(2)
- HTML Lists
- HTML Tables
- HTML Form Elements
- Links
- Divs
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1HebnyjDMsC-7-h2J3F5s-BxwDGwJ5fYZ?usp=sharing